The Digestive System
Food undergoes four types of processes in the body:
- Ingestion - Take in food through the mouth.
- Digestion - Broken into smaller particles that can be acted upon by various enzymes
- Absorption - Pass through cell membranes of the lining in the small intestine into the blood or lymph capillaries.
- Elimination - The removal of indigestible wastes through the anus, in the form of faeces.
Regions of the Digestive System
At its simplest, the digestive system is a tube running from mouth to anus.
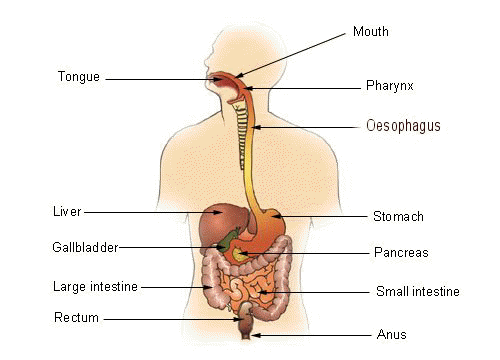
Regions of the digestive system can be divided into two main parts: the alimentary tract and accessory organs. The alimentary tract of the digestive system is composed of the:
- Mouth
- Pharynx
- Oesophagus
- Stomach
- Small and Large intestines
- Rectum and Anus
- Salivary Glands
-
- It has a cleansing action on the teeth.
- It moistens and lubricates food during mastication and swallowing.
- It dissolves certain molecules so that food can be tasted.
- Liver
-
- Bile production and excretion
- Excretion of bilirubin, cholesterol, hormones, and drugs
- Metabolism of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates
- Enzyme activation
- Storage of glycogen, vitamins, and minerals, and regulation of glucose levels
- Synthesis of plasma proteins, such as albumin, and clotting factors
- Blood detoxification and purification
- Conversion of ammonia, a by-product of metabolism, into a less toxic form called urea.
- Gallbladder - Storage reservoir for bile
- Pancreas
-
- Production of Insulin
- Production of Pancreatic juices
Common Digestive Problems
Haematemesis is the vomiting of fresh red blood or old darker blood often referred to as coffee grounds. The source is generally the upper gastrointestinal tract if the blood is fresh or from the stomach with the darker blood.
Peptic ulcer is a non-malignant ulcer of the stomach (called gastric ulcer) or duodenum (called duodenal ulcer).
Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas. It can occur periodically or chronically. The first sign may be a sudden, severe abdominal pain above the navel, which travels through to the back. Accompanying symptoms may include a slight fever, nausea, and vomiting.
Constipation is the term given for infrequent or difficult evacuation of small, hard stools, accompanied by mild abdominal discomfort. When the condition is chronic, it may include nausea, stomach rumbling, appetite loss, and malaise.
This list is not complete as there are many problems that can occur.
Management
Refer to the section Acute Abdominal Problems